Introduction: What is the Abductor Pollicis Brevis?
The abductor pollicis brevis is a small yet vital muscle located in the human hand. It plays a crucial role in hand movement, particularly in the ability to move the thumb away from the palm, which is essential for grasping objects and performing various tasks. Understanding the anatomy and function of the abductor pollicis brevis is important for healthcare professionals, fitness enthusiasts, and individuals experiencing hand discomfort. In this article, we will explore the abductor pollicis brevis, its function, related conditions, and how it impacts overall hand health.
The Anatomy of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Location and Structure of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis
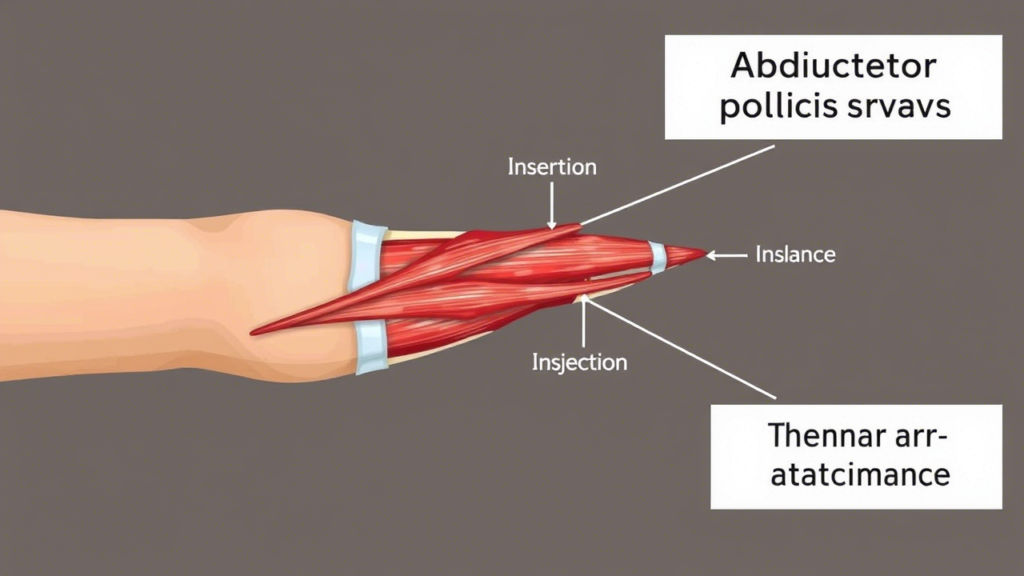
The abductor pollicis brevis is one of the muscles of the thenar eminence, a group of muscles located at the base of the thumb. These muscles are responsible for fine motor control and complex movements of the thumb, which are essential for tasks such as writing, typing, and gripping objects.
Anatomically, the abductor pollicis brevis originates from the flexor retinaculum and the scaphoid and trapezium bones of the wrist. It inserts into the proximal phalanx of the thumb. This position allows the muscle to perform its primary function: abduction of the thumb.
Function of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis
The primary role of the abductor pollicis brevis is to abduct the thumb—meaning it pulls the thumb away from the palm, which is a movement vital for grasping and pinching. Abduction is an essential component of many hand functions, including picking up objects, typing, and various activities that require dexterity and precision.
In addition to abduction, the abductor pollicis brevis also contributes to the opposition of the thumb, which is the ability to move the thumb across the palm to touch the other fingers. Opposition is a critical movement for many everyday tasks, such as writing, holding tools, or playing musical instruments.
The Importance of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis in Hand Health
Impact on Hand Function
The abductor pollicis brevis plays an indispensable role in hand function. Without its ability to abduct the thumb, many fine motor tasks would become significantly harder to perform. Its importance extends beyond simple grasping; without full abduction and opposition of the thumb, the hand loses its dexterity, leading to difficulty in handling objects and performing intricate tasks.
Conditions Affecting the Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Several conditions can impact the health and function of the abductor pollicis brevis. Carpal tunnel syndrome, for example, can affect the median nerve, which innervates this muscle. When the median nerve becomes compressed or irritated, it can lead to weakness or paralysis of the abductor pollicis brevis, making thumb movement difficult.
Another condition, de Quervain’s tenosynovitis, can lead to inflammation of the tendons around the thumb and wrist, affecting the muscle’s ability to function properly. Trauma or overuse injuries can also lead to damage to the abductor pollicis brevis, causing pain and weakness.
How to Maintain a Healthy Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Strengthening Exercises for the Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Keeping the abductor pollicis brevis strong and functional is essential for maintaining hand health. Certain exercises can help to strengthen this muscle and ensure its proper functioning. Simple activities like thumb stretches, thumb lifts, and resistance exercises using therapy putty can help improve thumb mobility and strength. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises can reduce the risk of muscle stiffness and improve range of motion.
Proper Ergonomics and Prevention of Injury
Proper ergonomics when using the hands—such as proper wrist positioning while typing or using tools—can help protect the abductor pollicis brevis from strain. It’s also important to avoid overuse or repetitive motions that place undue stress on the hand and thumb. Taking regular breaks, practicing good posture, and stretching the hands frequently can help prevent injuries.
The Role of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis in Fitness
For fitness enthusiasts, the health of the abductor pollicis brevis is important for exercises that involve gripping or lifting. Whether it’s lifting weights, rock climbing, or practicing yoga, thumb stability and strength are essential. Proper hand strength ensures that athletes can maintain control over equipment and avoid injury. As part of a full-body fitness routine, exercises that target the hands, such as grip-strengthening activities or thumb-focused stretches, can help improve overall performance.
Common Injuries and Disorders of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
As mentioned earlier, carpal tunnel syndrome is one of the most common conditions that can affect the abductor pollicis brevis. This syndrome occurs when the median nerve is compressed as it travels through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Symptoms include pain, numbness, and weakness in the thumb and fingers. Since the abductor pollicis brevis is innervated by the median nerve, individuals with carpal tunnel syndrome often experience difficulty with thumb abduction.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is an inflammation of the tendons that control thumb movement. This condition is commonly seen in individuals who engage in repetitive hand movements, such as texting, typing, or heavy lifting. The resulting inflammation can lead to pain and difficulty moving the thumb, and in some cases, it can affect the abductor pollicis brevis, leading to weakness or discomfort.
Tendonitis and Strain
Overuse or trauma to the thumb can cause tendonitis or muscle strain, affecting the performance of the abductor pollicis brevis. These injuries can be particularly troublesome for athletes or individuals who engage in activities requiring intense hand use. Treatment typically involves rest, ice, and stretching exercises to relieve pressure on the tendons.
Conclusion: The Vital Role of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis in Hand Function
The abductor pollicis brevis is a key muscle in the hand that enables essential movements like thumb abduction and opposition. It plays a vital role in the dexterity and strength required for everyday tasks, from gripping objects to performing fine motor activities. Understanding its anatomy, function, and common disorders can help individuals take better care of their hands and prevent injuries. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a fitness enthusiast, or someone experiencing discomfort in your hands, taking steps to strengthen and protect the abductor pollicis brevis is crucial for maintaining optimal hand health.
FAQ Section
1. What is the primary function of the abductor pollicis brevis?
The primary function of the abductor pollicis brevis is to abduct the thumb, allowing it to move away from the palm. This is essential for gripping, pinching, and other fine motor tasks.
2. Can the abductor pollicis brevis be injured?
Yes, injuries such as overuse, trauma, or conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or de Quervain’s tenosynovitis can affect the abductor pollicis brevis, leading to pain or weakness.
3. How can I strengthen the abductor pollicis brevis?
Exercises like thumb stretches, lifts, and resistance exercises can help strengthen the abductor pollicis brevis and maintain thumb mobility.
4. What is carpal tunnel syndrome, and how does it affect the abductor pollicis brevis?
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve is compressed, leading to weakness or paralysis of muscles like the abductor pollicis brevis, which can impair thumb movement.
5. Is the abductor pollicis brevis important for athletes?
Yes, the abductor pollicis brevis plays a crucial role in exercises that involve gripping, such as weightlifting or rock climbing. Strong and healthy thumb muscles are essential for proper control during these activities.
6. How can I prevent injuries to the abductor pollicis brevis?
Maintaining proper ergonomics, avoiding overuse, and regularly stretching and strengthening the hand can help prevent injuries to the abductor pollicis brevis.