Meta Title: Adductor Brevis Muscle: Anatomy, Function, Injuries & Treatment
Meta Description: Learn about the Adductor Brevis Muscle, its function, anatomy, common injuries, and effective treatment methods in this comprehensive guide.
Adductor Brevis Muscle: Anatomy, Function, Injuries & Treatment
Introduction
The Adductor Brevis Muscle is a crucial part of the human thigh, playing a significant role in hip movement and stability. This muscle is one of the three primary adductor muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh, assisting in various lower-body functions such as walking, running, and maintaining balance. Understanding its anatomy, function, and common injuries can help medical professionals, athletes, and individuals recovering from groin injuries manage and prevent complications.
This in-depth guide explores the Adductor Brevis Muscle, its function, structure, injuries, treatment options, and strengthening exercises, offering valuable insights for medical students, physiotherapists, and fitness professionals.
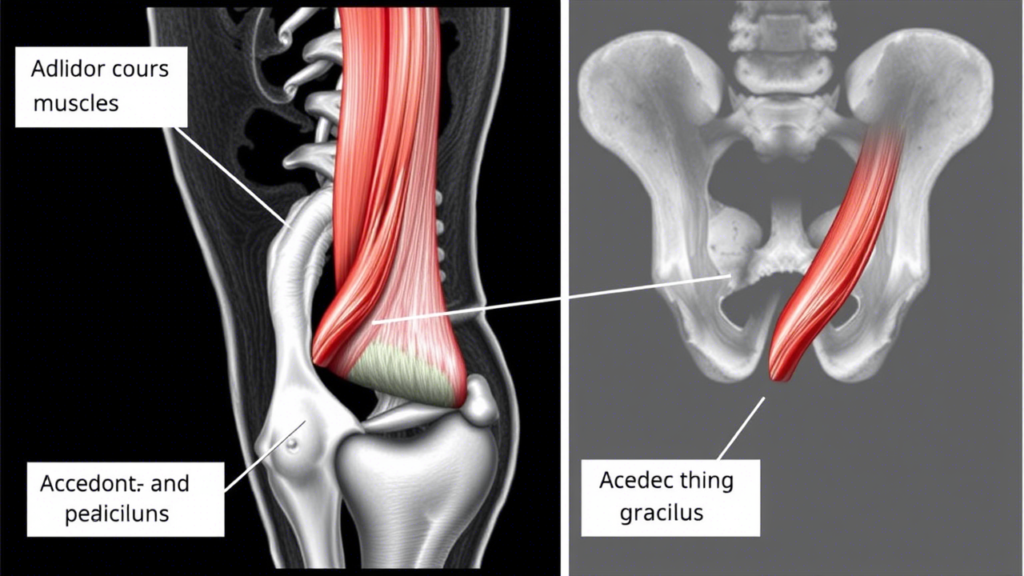
Anatomy of the Adductor Brevis Muscle
1. Location and Structure
The Adductor Brevis Muscle is situated in the medial compartment of the thigh. It originates from the anterior surface of the inferior pubic ramus and inserts into the pectineal line and proximal part of the linea aspera of the femur. It lies between the Adductor Longus and Adductor Magnus, partially covered by both muscles.
2. Blood Supply and Innervation
- Blood Supply: The Obturator Artery primarily supplies the muscle, ensuring adequate oxygenation and nutrient flow.
- Innervation: The Obturator Nerve (L2, L3, L4) provides the necessary motor function, allowing effective contraction and relaxation of the muscle.
3. Role in the Muscular System
The Adductor Brevis Muscle works alongside other adductors, such as the Adductor Longus, Adductor Magnus, and Gracilis, to provide stability and strength during movement.
Function of the Adductor Brevis Muscle
1. Hip Adduction
The primary function of the Adductor Brevis Muscle is to bring the thigh closer to the body’s midline, a movement known as hip adduction. This function is crucial in walking, running, and various athletic activities.
2. Assisting Hip Flexion and Rotation
Besides adduction, the muscle contributes to hip flexion and medial rotation, aiding in movements that require precise lower-body control.
3. Stabilization of the Pelvis
The Adductor Brevis Muscle plays a key role in stabilizing the pelvis during movement, ensuring balance and coordination.
Common Injuries of the Adductor Brevis Muscle
1. Adductor Strain or Tear
A strain occurs when the muscle fibers stretch beyond their limits. Severe cases may result in partial or complete tears, causing significant discomfort and mobility issues.
- Symptoms: Sharp pain in the inner thigh, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the leg.
- Causes: Overuse, sudden movements, or inadequate warm-ups.
2. Tendinopathy
Chronic overuse of the Adductor Brevis Muscle can lead to tendinopathy, characterized by tendon degeneration and pain.
- Symptoms: Gradual onset of pain, tenderness, and stiffness.
- Causes: Repetitive stress from running, jumping, or heavy lifting.
3. Groin Pain Syndrome
This condition results from chronic stress or repetitive strain on the groin muscles, including the Adductor Brevis Muscle.
- Symptoms: Persistent groin pain, weakness, and discomfort in daily activities.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Adductor Brevis Muscle Injuries
1. Diagnosis Methods
- Physical Examination: Doctors assess tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or ultrasound helps confirm muscle tears or tendinopathy.
2. Treatment Approaches
- Rest and Ice Therapy: Reduces inflammation and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises improve flexibility and recovery.
- Medications: NSAIDs help manage pain and swelling.
- Surgical Intervention: Severe muscle tears may require surgical repair.
Strengthening and Rehabilitation Exercises
1. Hip Adduction Exercises
- Seated and standing adduction movements enhance muscle endurance and strength.
2. Resistance Band Workouts
- Using resistance bands improves flexibility and prevents re-injury.
3. Stretching Routines
- Regular stretching reduces muscle tightness and promotes mobility.
Preventing Adductor Brevis Muscle Injuries
- Warm-Up Before Exercise: Increases blood flow to the muscles.
- Strength Training: Builds muscle resilience and reduces the risk of strains.
- Proper Hydration and Nutrition: Supports muscle recovery and function.
FAQs
1. What is the main function of the Adductor Brevis Muscle?
The Adductor Brevis Muscle primarily aids in hip adduction, helping bring the thigh towards the midline.
2. How do you strengthen the Adductor Brevis Muscle?
Incorporating hip adduction exercises, resistance band workouts, and stretching routines can effectively strengthen the muscle.
3. What are the common injuries associated with the Adductor Brevis Muscle?
Common injuries include adductor strains, tendinopathy, and groin pain syndrome.
4. How is an Adductor Brevis Muscle strain treated?
Treatment involves rest, ice therapy, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery.
5. Can the Adductor Brevis Muscle cause groin pain?
Yes, injuries or overuse can lead to groin pain and mobility issues.
6. How can I prevent Adductor Brevis Muscle injuries?
Warming up before exercise, strength training, and maintaining hydration can help prevent injuries.
7. Can a torn Adductor Brevis Muscle heal without surgery?
Mild to moderate tears can heal with conservative treatments, while severe cases may require surgical intervention.
8. What sports commonly lead to Adductor Brevis Muscle injuries?
Soccer, basketball, running, and weightlifting pose higher risks due to repetitive leg movements.
Conclusion
The Adductor Brevis Muscle plays a vital role in hip movement, stability, and overall lower-body function. Whether you’re an athlete, physiotherapist, or recovering from an injury, understanding its anatomy, function, and treatment methods can help in preventing and managing muscle-related conditions. By following proper exercise techniques and preventive measures, individuals can maintain optimal muscle health and mobility.